Quiz 4 - Types and Structures of Crystals | Liquids and Solids
General Chemistry 2 - Quiz 4 - Types and Structures of Crystals
For the same atoms at the lattice points, which lattice exhibits the lowest density?
Density in a crystal lattice depends on how closely the atoms are packed together. The simple cubic lattice has the lowest packing efficiency, with atoms occupying only about 52% of the available space. This means it has the lowest density compared to other lattice types.
In contrast, the body-centered cubic (BCC) and face-centered cubic (FCC) lattices have higher packing efficiencies, at approximately 68% and 74%, respectively. The hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure also has a high packing efficiency similar to FCC.
The arrangement of ions in a solid is best investigated by means of:
X-ray crystallography is the most effective technique for determining the arrangement of ions (or atoms) in a solid. It involves directing X-rays at a crystal and analyzing the pattern of diffraction that results, which provides detailed information about the positions of atoms or ions within the crystal lattice.
An oxide of rhenium crystallizes with eight rhenium atoms at the corners of the unit cell and 12 oxygen atoms on the edges between them. What is the formula of this oxide?
To determine the formula of the rhenium oxide, we need to analyze the contribution of atoms within the unit cell.
Rhenium atoms:
- There are 8 rhenium atoms at the corners of the unit cell.
- Each corner atom is shared by 8 adjacent unit cells, so the contribution of each rhenium atom to a single unit cell is .
- Total contribution of rhenium atoms to the unit cell: 8 x = 1 rhenium atom
Oxygen atoms:
- There are 12 oxygen atoms located on the edges of the unit cell.
- Each edge is shared by 4 adjacent unit cells, so the contribution of each oxygen atom to a single unit cell is .
- Total contribution of oxygen atoms to the unit cell: 12 x = 3 oxygen atoms
Thus, the formula of the oxide is ReO3.
Which statement about atoms arranged in a body-centered cubic (bcc) crystal structure is correct?
- Option A is incorrect because the body-centered cubic (bcc) structure is observed in several metallic elements, such as iron at certain temperatures, chromium, and tungsten.
- Option B is incorrect because the cubic closest-packed (ccp) structure is another name for the face-centered cubic (fcc) structure, not the bcc structure.
- Option C is correct. In a bcc structure, there is one atom at each corner of the cube and one atom in the center of the cube. Each corner atom is shared by eight adjacent unit cells, so the total number of atoms in a bcc unit cell is 8 x + 1 = 2 atoms.
- Option D is incorrect because in a bcc structure, each atom has 8 nearest neighbors, not 6.
Which solid has the highest melting point?
- OF2 (Oxygen difluoride) and ClO2 (Chlorine dioxide) are molecular compounds with relatively weak intermolecular forces, leading to lower melting points.
- MgF2 (Magnesium fluoride) is an ionic compound, which typically has a high melting point due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions.
- SiO2 (Silicon dioxide) is a network covalent solid, where each silicon atom is bonded to oxygen atoms in a strong, extensive 3D lattice. This type of bonding gives SiO2 an exceptionally high melting point, much higher than that of ionic or molecular compounds.
A portion of the structure of solid potassium is shown below. In what type of unit cell are the atoms arranged?
The image shows a structure where the spheres (atoms) appear to be arranged with one atom at each corner of the cube and one atom in the center of the cube. This arrangement is characteristic of a body-centered cubic (BCC) unit cell.
In a BCC structure, there is one atom at each of the eight corners of the cube and one atom in the center. This is a common structure for alkali metals like potassium.
What is the formula of the oxide whose unit cell is shown?
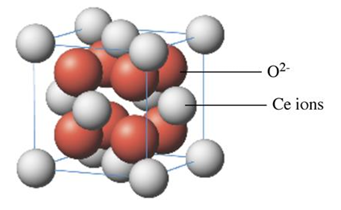
In the unit cell shown, there are:
- 8 cerium ions at the corners. Each corner ion is shared by 8 adjacent unit cells, so the contribution of cerium to the unit cell is: 8 x = 1 cerium ion
- 6 cerium ions at the face centers. Each face-centered ion is shared by 2 adjacent unit cells, so the contribution of cerium to the unit cell is: 6 x = 3 cerium ions
- 8 oxygen ions inside of the unit cell. The contribution of oxygen to the unit cell is: 8 oxygen ions
This indicates that the unit cell contains 4 cerium ions and 8 oxygen ions, which corresponds to the empirical formula CeO2.
The melting point of silicon dioxide (1713 oC) is higher than the melting point of silicon (1414 ºC). What is the best explanation for this difference?
Silicon dioxide (SiO2) has a higher melting point than silicon (Si) primarily because the bonds between silicon and oxygen in SiO2 are stronger than the bonds between silicon atoms in pure silicon. Silicon dioxide forms a strong covalent network structure with Si-O bonds, which require a significant amount of energy to break, resulting in a higher melting point. In contrast, silicon atoms are bonded to each other in a lattice structure, and these Si-Si bonds are not as strong as Si-O bonds.
How many nearest neighbors does each silicon atom have in solid Si?
In solid silicon, which crystallizes in a diamond cubic structure, each silicon atom is covalently bonded to 4 other silicon atoms. These 4 atoms are the nearest neighbors, forming a tetrahedral arrangement around each silicon atom.
Diamond is an example of what kind of solid?
Diamond is a classic example of a network covalent solid. In diamond, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement, forming a continuous 3D network. This strong bonding throughout the structure gives diamond its remarkable hardness and high melting point.
.svg)